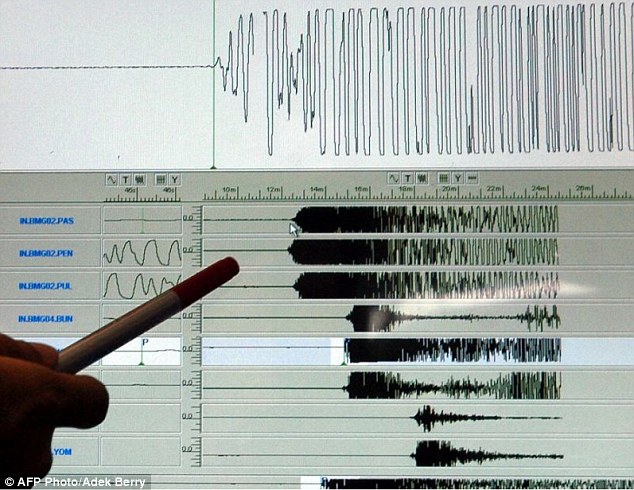
Using the seismic equipment, researchers have detected a rare deep-tremor on the ocean floor in Japan for the first time. They have managed to trace its location to a distant and powerful storm between Greenland and Iceland.
The findings could help experts learn more about the Earth’s inner structure and improve the detection of earthquakes and oceanic storms.
The storm that caused the deep-Earth tremor was a ‘weather bomb’ that struck over the North Atlantic. This is a small but potent storm in which pressure quickly builds, creating a more vigorous storm. As the storm hit, groups of waves pounded the ocean floor between Greenland and Iceland. These subtle waves run through the Earth and can be detected in distant places.
The researchers used seismic equipment at 200 sites on both land and on the seafloor in Japan to track the tremors. Their readings showed that they were secondary (S) wave microseisms – or very faint tremors.
Unlike primary (P) waves, which are usually detected during major hurricanes, S waves are slow, and only move through rock. This marks the first time scientists have observed an S wave.
In an accompanying article, Peter Gerstoft and Peter Bromirski, from the University of California in San Diego said that the discovery ‘gives seismologists a new tool with which to study Earth’s deeper structure.’
While the deep-sea tremor was discovered, these should not be mistaken as an earthquake.
In an article for The Conversation, David Rotheray, Professor of Planetary Geosciences at The Open University, said: ‘There’s a danger that this research could be misreported as an Atlantic storm causing an earthquake in Japan.
‘The reality is that the Japanese scientists detected an intensification of the usual background hum.’
However, while the tremors in Japan were not an earthquake, the findings, which are published in Science, could improve the understanding of Earth’s inner core, and could be used to improve the detection of earthquakes in the future.
Professor Rotheray added: ‘Knowing we can isolate the signals from storms could be particularly useful because the region where the weather bomb occurred almost never experiences earthquakes.
‘So storms elsewhere may in time prove equally useful.’
Sourced from Daily Mail, Featured image courtesy: AFP