South Africa has decided to withdraw from the International Criminal Court following a dispute last year over a visit by Sudanese President Omar al-Bashir who is wanted by the tribunal for alleged war crimes, crimes against humanity and genocide.
A copy of the “Instrument of Withdrawal,” dated Wednesday and signed by Foreign Minister Maite Nkoana-Mashabane, was obtained yesterday by The Associated Press.
It states that South Africa “has found that its obligations with respect to the peaceful resolution of conflicts at times are incompatible with the interpretation given by the International Criminal Court of obligations contained in the Rome Statute” which established the court.
Under the Rome Statute, South Africa as a party to the ICC has an obligation to arrest anyone sought by the tribunal.
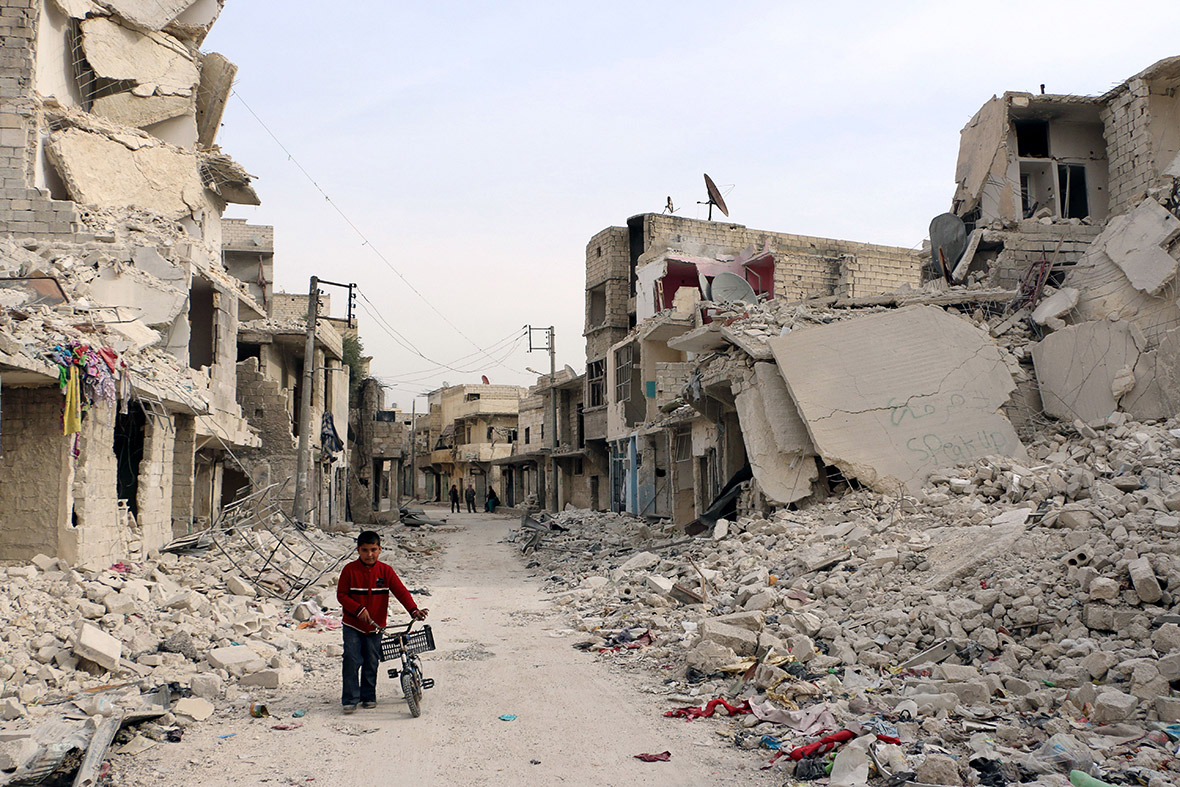
The charges against al-Bashir stem from the bloodshed in Sudan’s western Darfur region which began in 2003 when rebels took up arms against the government in Khartoum, accusing it of discrimination and neglect. The United Nations says 300,000 people have died in the conflict and 2.7 million have fled their homes.
In June 2015, Al-Bashir went to South Africa to attend an African Union summit but the government didn’t arrest him. A provincial court ordered him to remain in the country while judges deliberated on whether he should be arrested on the ICC warrants, but al-Bashir left for Sudan before the court ruled that he should indeed be arrested. The Supreme Court of Appeal later described the government’s failure to arrest al-Bashir as “disgraceful conduct.”
From Agencies, Feature image courtesy humanityunited